Bitcoin’s energy consumption is legendary. At its peak, the network used more electricity than entire countries like Argentina or the Netherlands. For many investors and innovators, this staggering environmental cost has become the elephant in the room—an existential threat to the long-term viability of decentralized finance. But what if there was a better way? A way to secure a blockchain network that doesn’t involve warehouses of power-hungry computers solving puzzles?
This is the very problem that Proof-of-Stake blockchains were designed to solve.
Forget everything you know about crypto “mining.” Proof-of-Stake (PoS) represents a fundamental paradigm shift in how blockchain networks achieve consensus, offering a compelling vision for a more scalable, efficient, and sustainable decentralized future.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive deep into the world of Proof-of-Stake. You’ll learn exactly how it works, its critical advantages over the older Proof-of-Work model, its potential drawbacks, and which projects are leading the charge. Understanding this technology is no longer optional for serious crypto investors; it’s essential.
First, What Is a Consensus Mechanism?
Before we can appreciate the innovation of PoS, we need to understand the problem it solves. A blockchain is a distributed ledger, meaning copies of it are held by numerous participants all over the world. A consensus mechanism is the set of rules that allows these participants to agree on the state of the ledger without needing to trust each other.
It’s the “engine” that ensures every transaction is valid and that everyone has the same version of the truth, preventing issues like double-spending. The very first and most famous consensus mechanism is Proof-of-Work (PoW), used by Bitcoin.
The Challenge with Proof-of-Work (PoW)
In a PoW system, participants called “miners” compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles. The first one to find the solution gets to add the next “block” of transactions to the chain and is rewarded with new coins.
- Massive Energy Consumption: This competition requires immense computational power, leading to the high energy usage we mentioned earlier.
- Specialized Hardware: Over time, PoW mining has become dominated by entities that can afford expensive, specialized hardware (ASICs), leading to concerns about centralization.
- Scalability Issues: The puzzle-solving process can be slow, limiting the number of transactions a network can process per second (like with Bitcoin’s ~7 TPS).
For blockchain technology to achieve mainstream adoption, it needed a more efficient and scalable engine.
Enter Proof-of-Stake (PoS): A Greener, Faster Solution
Proof-of-Stake blockchains abandon the race for computational power. Instead of miners, PoS networks are secured by validators.
Instead of proving they have expended computational work, validators are chosen to create new blocks based on the number of coins they have “staked.” You can think of staking as putting up a security deposit. By locking up a certain amount of the network’s native cryptocurrency, a validator demonstrates they have a vested interest—a “stake”—in the network’s health and security.
If they act honestly and validate transactions correctly, they are rewarded. If they act maliciously, they can lose a portion or all of their staked funds. This economic incentive—the carrot of rewards and the stick of penalties (slashing)—is what secures the network.
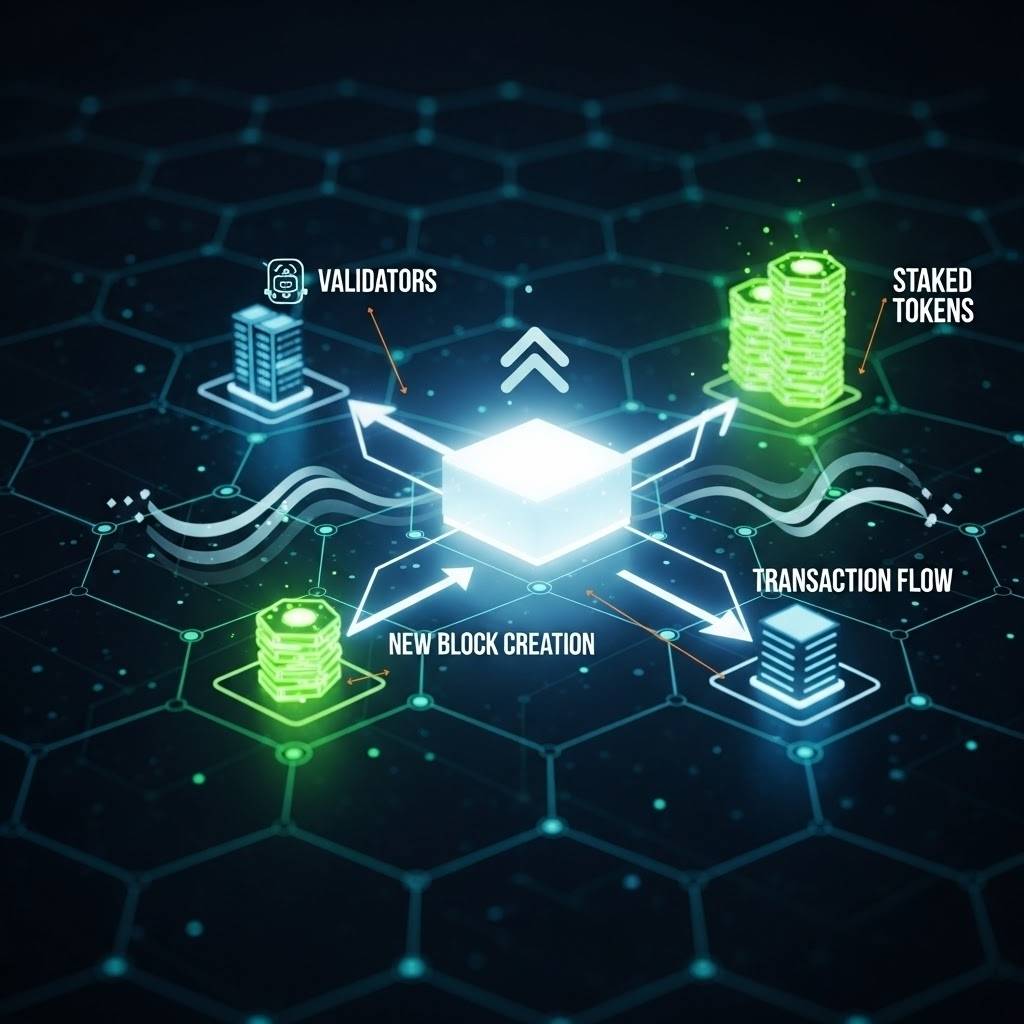
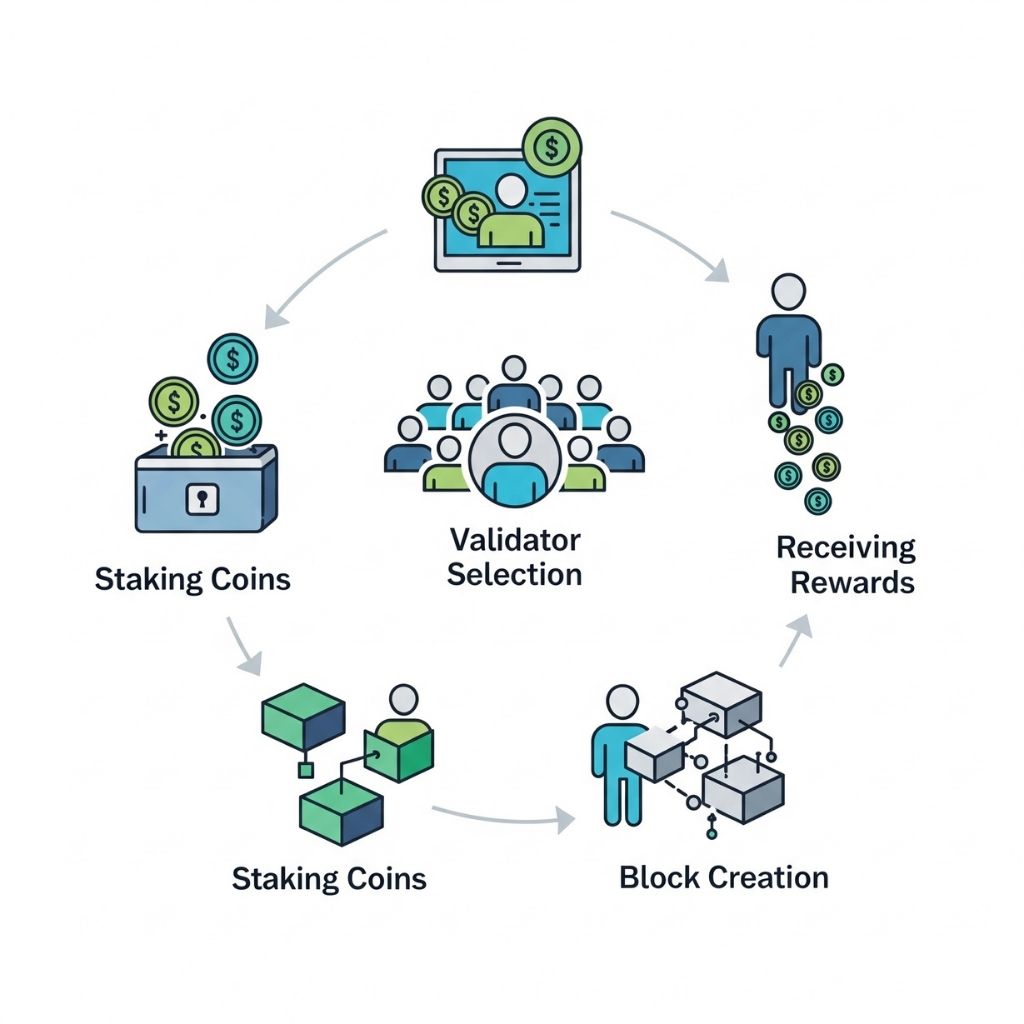
How Do Proof-of-Stake Blockchains Actually Work?
While different PoS chains have unique variations, the core process generally follows these steps.
The Role of Validators
Validators are the backbone of a PoS network. They are responsible for:
- Processing Transactions: Verifying that transactions are legitimate.
- Creating New Blocks: Bundling verified transactions into new blocks.
- Maintaining Network Security: Participating in the consensus protocol to agree on the single true version of the blockchain.
To become a validator, a user must lock up, or stake, a minimum amount of the network’s native cryptocurrency. For example, to become a full validator on the Ethereum network, you must stake 32 ETH.
The Staking Process
But what if you don’t have enough coins to be a full validator or don’t want to run the required hardware? Most Proof-of-Stake blockchains offer a solution: delegated staking.
Users can delegate their smaller stake to a professional validator running a “staking pool.” In return for contributing to the pool’s total stake, they receive a proportional share of the rewards, minus a small fee paid to the pool operator. This makes participation in network security accessible to a much wider range of users. Learn more about crypto staking strategies
Block Creation and Rewards
Unlike PoW where everyone is competing at once, in PoS, a validator is pseudo-randomly selected to create the next block. The probability of being chosen is often proportional to the size of their stake—the more you stake, the higher your chance of being selected.
When a validator successfully proposes a block that other validators attest to as valid, they receive a reward, typically composed of transaction fees and sometimes a small amount of newly created cryptocurrency. This reward is the incentive for participating and securing the network.
Key Advantages of Proof-of-Stake
The shift to PoS offers several transformative benefits that are crucial for the evolution of blockchain technology.
- Energy Efficiency: This is the most significant advantage. By eliminating the need for intensive computation, PoS networks consume a tiny fraction of the energy of PoW networks. The Ethereum Merge, which saw the network transition from PoW to PoS, [external link: reduced Ethereum’s energy consumption by over 99.95%].
- Greater Scalability: PoS consensus can often be reached faster, allowing for higher transaction throughput and lower fees. This makes PoS chains better suited for applications like DeFi and NFTs that require high performance.
- Lower Barriers to Entry: Users don’t need to buy expensive mining rigs. They can participate by staking, often with any amount of crypto through staking pools. This promotes greater decentralization of network participation.
- Stronger Security: The financial stake that validators have locked in the system creates a powerful disincentive against attacks. An attacker would need to acquire a massive amount of the cryptocurrency (typically over 51% of the total staked amount) to compromise the network, an incredibly expensive and self-defeating endeavor.
Potential Drawbacks and Criticisms of PoS
No system is perfect, and it’s important for investors to understand the potential downsides of Proof-of-Stake blockchains.
- “The Rich Get Richer” Concern: Since those with a larger stake have a higher chance of being chosen to create blocks and earn rewards, critics argue that PoS can lead to wealth concentration over time.
- Nothing-at-Stake Problem: This is a theoretical issue where, in the event of a chain fork, validators have nothing to lose by validating on both chains, potentially causing network instability. Modern PoS protocols have largely solved this through “slashing” mechanisms.
- Validator Centralization: While the barrier to entry is lower for users, running a validator node still requires technical expertise and can be costly. This could lead to a concentration of power among a few large staking providers.
PoS vs. PoW: A Head-to-Head Comparison
| Feature | Proof-of-Work (PoW) | Proof-of-Stake (PoS) |
| Method | Miners solve computational puzzles | Validators are chosen based on staked coins |
| Energy Use | Extremely high | Very low (~99.9% less) |
| Hardware | Specialized, expensive ASICs | Standard server-grade hardware |
| Scalability | Lower transaction throughput | Higher transaction throughput |
| Participation | Requires mining hardware and cheap electricity | Requires owning and staking cryptocurrency |
| Security Model | Secured by computational power (hashrate) | Secured by economic incentives (value at stake) |
| Key Examples | Bitcoin, Litecoin, Dogecoin | Ethereum, Cardano, Solana, Polkadot |
Export to Sheets
Prominent Proof-of-Stake Blockchains to Watch
The PoS ecosystem is vibrant and growing. Here are a few of the most significant projects that investors should be aware of:
- Ethereum (ETH): The largest smart contract platform, Ethereum’s successful “Merge” to Proof-of-Stake in 2022 was a landmark event for the entire crypto industry.
- Cardano (ADA): A third-generation blockchain built from the ground up on a peer-reviewed, research-driven approach to PoS.
- Solana (SOL): Known for its incredibly high throughput and low transaction costs, Solana uses a unique consensus mechanism called Proof-of-History, which is layered on top of PoS.
- Polkadot (DOT): A multi-chain network designed for interoperability, allowing different blockchains to communicate. It uses a nominated Proof-of-Stake (NPoS) system.
Understanding the nuances of each project’s PoS implementation is crucial, as it directly impacts their performance, security, and investment potential.
Navigating the PoS Landscape with Scentia Research Group
The transition from Proof-of-Work to Proof-of-Stake is more than just a technical upgrade; it’s a fundamental shift in the economic and security models of digital assets. For investors, this creates both immense opportunity and significant complexity.
Evaluating the strength of a Proof-of-Stake blockchain requires a deep dive into its tokenomics, validator distribution, slashing parameters, and governance structure. Surface-level analysis is no longer enough to build a resilient and high-growth crypto portfolio.
This is where Scentia Research Group provides a critical edge. Our team of analysts specializes in dissecting the complex technical and economic layers of leading blockchain projects. We go beyond the hype to provide data-driven insights that help our clients understand the true risks and rewards of the evolving digital asset landscape. We believe that a deep understanding of core technologies like Proof-of-Stake is the foundation of any successful crypto investment strategy. Learn More About Scentia Research Group’s methodology
The Future is Staked
Proof-of-Stake blockchains are not just an alternative to Proof-of-Work; they are the next logical step in the evolution of decentralized technology. By solving the critical issues of energy consumption and scalability, PoS paves the way for blockchain to become the backbone of a new generation of financial services, creative economies, and global networks.
As this technology continues to mature, the projects that master its implementation will be best positioned for long-term growth and adoption.
Are you ready to build a crypto portfolio based on deep, fundamental research?
Contact the experts at Scentia Research Group today for a personalized consultation and discover how our insights can help you navigate the future of finance.